As a result in the long run only one quantity is to be supplied. The nature of the short-run and long-run aggregate supply curves given by AS and Yn implies that changes in the aggregate demand curve such as fiscal and monetary policy shifts or changes in expectations which affect investment have an effect on output in the short run but not in the long run.
Aggregate Supply Aggregate Supply And Aggregate Demand Sparknotes
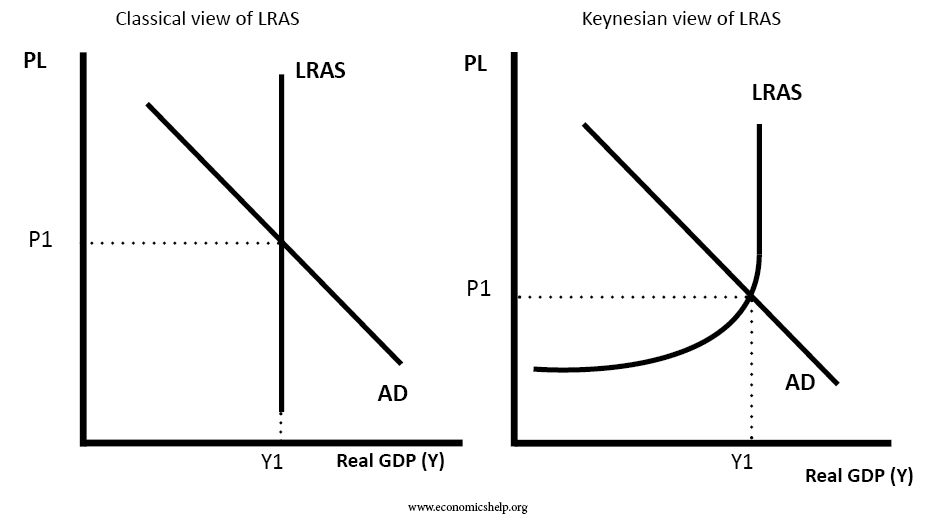
Therefore it is perfectly vertical reflecting economists belief that the changes in aggregate demand result in a temporary difference in an economys output.
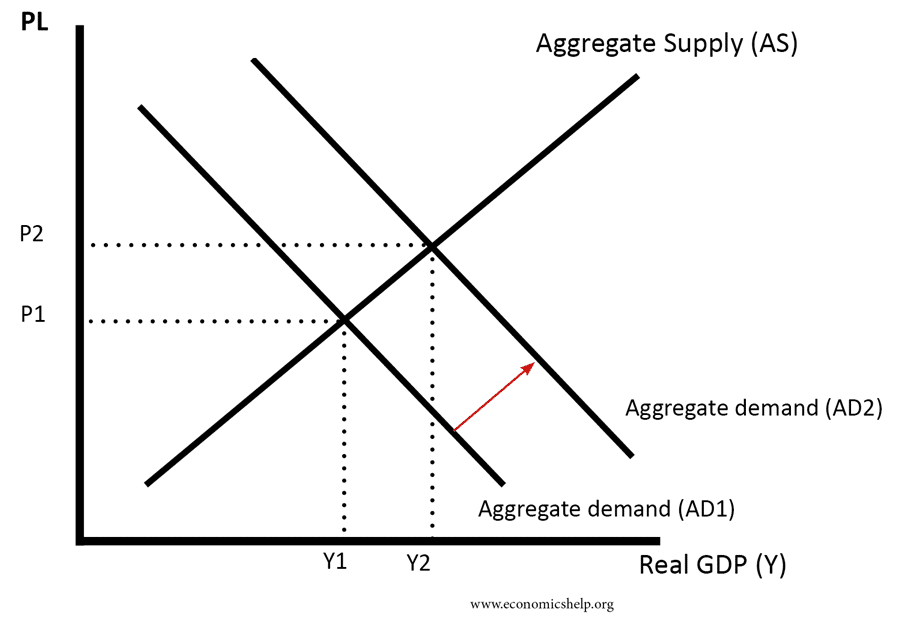
. A model that shows what determines real GDP and the aggregate price level through the interaction between total spending on domestic goods and services ie aggregate demand and total production by businesses ie. When the economy reaches its level of full capacity full employment when the economy is on the production possibility frontier the aggregate supply curve. With aggregate demand at AD1 and the long-run aggregate supply curve as shown real GDP is 12000 billion per year and the price level is 114.
The aggregate supply curve shifts to the left as the price of key inputs rises making a combination of lower output higher unemployment and higher inflation possible. What is the version of aggregate supply that allows for changes in both product prices and resource prices is the. Aggregate supply is the total value of goods and services produced in an economy.
The version of aggregate supply that allows for changes in both product prices and resource prices is the surplus and the price level will fall if at a particular price level real domestic output from producers is greater than real domestic output. The aggregate supply curve shows the amount of goods that can be produced at different price levels. This is a negative supply shock.
Supply and Demand The laws of supply and demand are microeconomic concepts that state that in efficient markets the quantity supplied of a good and quantity. Explain the forces that naturally press an economy to long-run equilibrium. The aggregate supply curve can also shift due to shocks to input goods or labor.
When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level a greater quantity of real GDP is produced. The long-run aggregate supply LRAS curve is static. With more resources it is possible to produce more final goods and services and hence the natural level of real GDP increases.
The version of aggregate supply that allows for changes in both product prices and resource prices is the. Create and interpret graphs of the aggregate demandaggregate supply model and describe the effects of changes in either upon price level employment and output. This module discusses two of the most important supply shocks.
This is called a positive supply shock. The first is the sticky-wage model. A second factor that causes the aggregate supply curve to shift is economic growth.
When the AS curve shifts to the left then at every price level a lower quantity of real GDP is produced. But applied at a macroeconomic scale. 1 Easy Learning Objective.
Changes in Aggregate Supply A shift in aggregate supply can be attributed to many variables including changes in the size and quality of labor technological innovations an increase in wages an. The second is the worker-misperception model. Positive economic growth results from an increase in productive resources such as labor and capital.
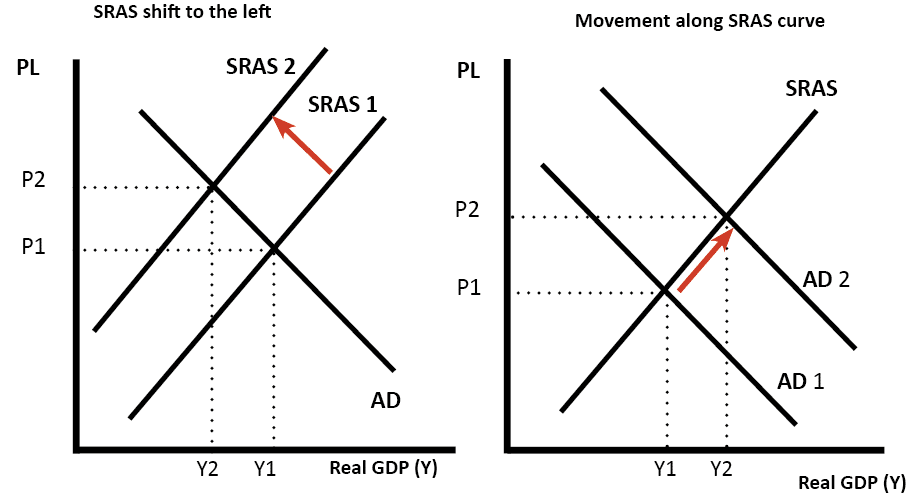
The Short-run Aggregate Supply SRAS. The third is the imperfect-information model. The original equilibrium E0 is at the intersection of AD and SRAS0.
Shifts in Aggregate Supply a The rise in productivity causes the SRAS curve to shift to the right. For example an unexpected early freeze could destroy a large number of agricultural crops a shock that would shift the AS curve to the left since there would be fewer. When SRAS shifts right then the new equilibrium E1 is at the intersection of AD and SRAS1 and then yet another equilibrium E2 is at the intersection of AD and SRAS2.
The version of aggregate supply that allows for changes in both product prices and resource prices is the. If aggregate demand increases to AD2 long-run equilibrium will be reestablished at real GDP of 12000 billion per year but at a higher price level of 118. As the labor force and capital stock increase in availability aggregate supply increases at every price level shifting aggregate supply to the right to SRAS 1.
Aggregate supply Modification adaptation and original content. Utilize activities and lessons from the AP Macro Fourth Edition to prepare students for AP tests. Aggregate supply and demand refers to the concept of supply and demand.
The difference between M1 and M2 is that. Aggregate supply and aggregate demand are both plotted against the aggregate price level in a nation. The former includes time deposits.
If aggregate demand decreases to AD3 long. Level 1 Remember Difficulty. When an economy experiences stagnant growth and high inflation at.
With a Keynesian aggregate supply curve an increase in aggregate demand affects only output as long as the economy is below full-employment output whereas an increase in aggregate supply has no effect upon either the price level or output when aggregate demand intersects aggregate supply in the horizontal portion of the curve see Example 45. 12-02 Define aggregate supply AS and explain the factors that cause it to change. While the long run aggregate supply curve is vertical the short run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping.
There are four major models that explain why the short-term aggregate supply curve slopes upward. Aggregate demandaggregate supply model. Changes in Government Action For example adopting policies that impose heavy taxes remove subsidies from local production or impose restrictive regulations can shift aggregate supply in the short.

What Is Aggregate Supply And Demand Explained Bohatala
Aggregate Supply Economics Help

0 Comments